CE MDR
In February 2017, the proposal of the Regulation (EU) 2017/745 on Medical Devices (MDR) was released. In March of the same year, the EU member states voted unanimously to agree to the MDR. On May 5, 2017, the EU’s Official Journal officially announced the contents of the MDR. The new MDR will replace the current Council Directive 90/385/EEC on Active Implantable Medical Devices (AIMDD) (1990) and Council Directive 93/42/EEC on Medical Devices (MDD) (1993). The MDR, which was originally planned to be formally implemented on May 26, 2020, will be postponed to May 26, 2021 due to the impact of the global 2019-nCoV epidemic.

During this period, the following MDD certificate-related activities can still be carried out, such as product changes, and application for new MDD accounts within one year; activities related to the renewal of the existing MDD client certificates; application for the renewal of the existing MDD client certificates (including application for the renewal in advance); application for the major changes to the existing MDD clients. Although the formal implementation of the MDR has been postponed, there are exceptions, such as:
· The deadline for launching the MDD products is still May 26, 2024
· The deadline for supplying the MDD products is still May 26, 2025
In terms of the impact on manufacturers and products, the 93/42 EEC Directive and the MDR almost have the same basic regulatory requirements. The existing requirements are not deleted, but new requirements are added to the MDR. Compared with the current 93/42 Directive, the MDR emphasizes the safety of the life cycle method and is supported by the clinical data. The MDR has put forward stricter requirements for the designation of the notified bodies, and the national competent authorities and committees have strengthened the control and monitoring. The MDR reclassifies certain devices to make the scope wider. For example, the MDR clearly covers all devices used for cleaning, disinfecting or sterilizing other medical devices (Article 2.1); disposable medical devices (Article 17); and certain non-medical devices (Annex XVI). The MDR also covers the medical devices sold on the Internet and the medical devices used to provide remote diagnosis or treatment services (Article 6). The MDR has introduced a clinical evaluation consultation procedure (Article 54) conducted by an independent expert panel for some Class IIb devices and implantable Class II devices.

The new unique device identification system (UDI system) (Article 27) will effectively enhance the traceability and effectiveness of post-market safety-related activities.
The MDR will also increase the transparency and disclose the information about the equipment and research. The new European Database on Medical Devices (Eudamed) will play a central role in providing data and increasing the quantity and quality of data (Article 33).
The implementation date of the MDR in 2021 is approaching. How to obtain the MDD certificate before the end of the transition period and how to obtain the MDR certificate quickly are the major concerns. Shanghai SUNGO has an excellent team of consultants and rich case experience.
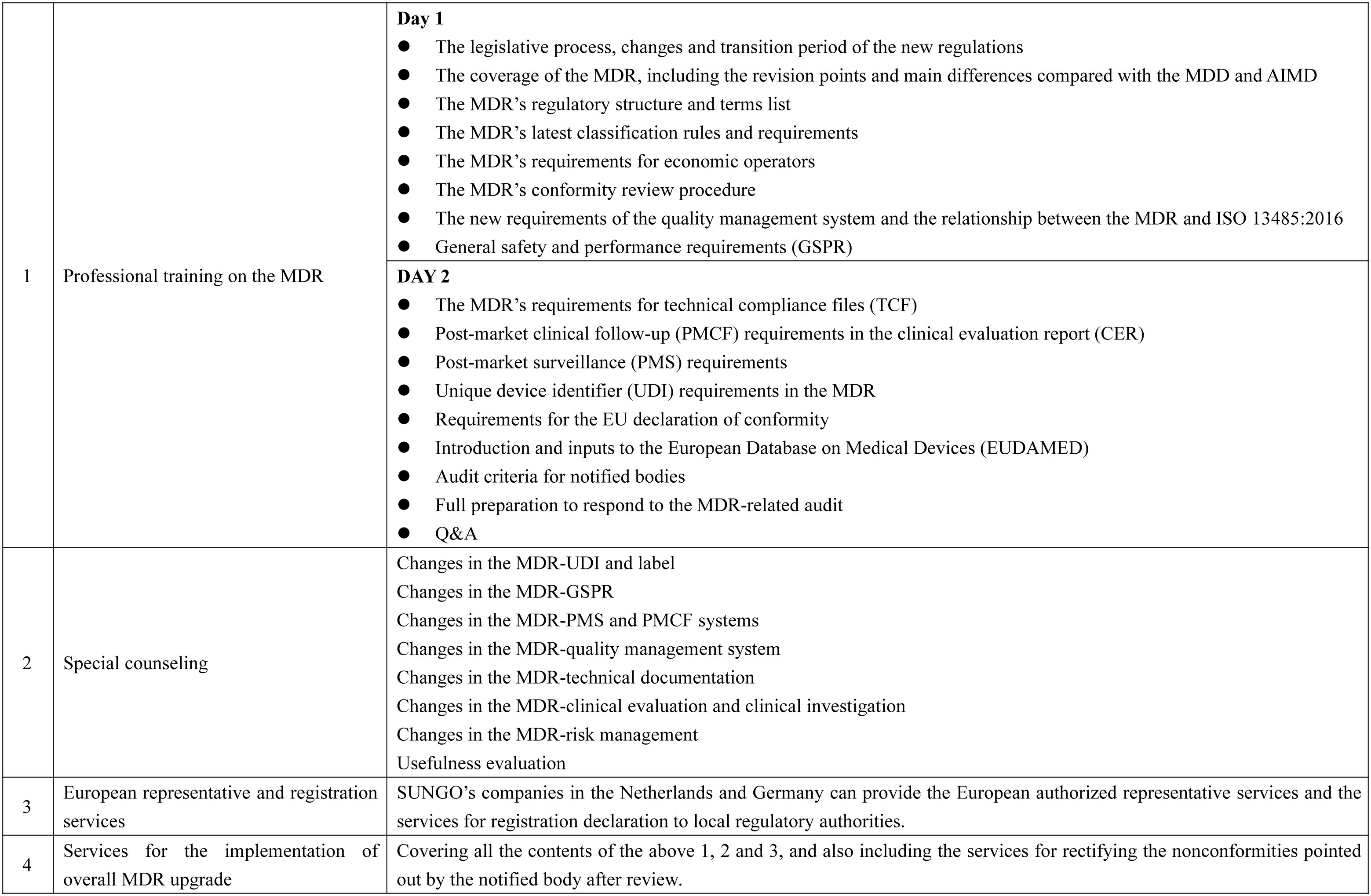
Our consulting services
Our service process