ISO9001&13485 Certification

I. Project introduction
The establishment, implementation and third-party certification of the quality management system are one of the ways to enhance the corporate image, gain the external trust, and reduce the cost of trust. Our company provides the ISO9001 and ISO13485 quality management system consulting services, and can provide the corresponding system consulting services based on the special requirements of different countries and regions for market access.
Core idea of ISO9001
ISO9001 is one of the ISO9000 series standards formulated by ISO/TC176. Its vision is to make the ISO90001 standard “become an integral part of the organization’s initiative to achieve sustainable development, and be recognized and respected worldwide”. Its core idea is continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
The ISO9001:2016 standard is based on the risk thinking and emphasizes the leadership of the top management. The quality management system starts from understanding the internal and external environments of the organization and identifies the opportunities and challenges the organization faces. The PDCA method is applied cyclically, continuous improvement is made, and the focus is placed on the organizational performance and the expected results of the quality management system; that is, the products and services shall continuously meet the customer and legal requirements.

Relationship between ISO9001 and product certification
The ISO9001 standard specifies a quality management system for the following organizations: a) it needs to be proved that the organization has the ability to stably provide products and services that meet the requirements of customers and applicable laws and regulations; b) through the effective application of the system, including the process of continuous system improvement, and ensuring the conformity to the requirements of customers and applicable laws and regulations, the organization can enhance the customer satisfaction.
Product certification is the process to approve the products that meet laws, regulations and standards. The ISO9001 standard provides the ability to steadily and continuously ensure the product quality. During the product certification audit, it is usually required to establish a quality management system to ensure this ability. For example, the quality system audit of Mode D of the EU’s PPE Directive is implemented in accordance with the ISO9001 standard.
Special requirements of ISO13485
ISO13485 is derived from but independent of ISO9001. It is applicable to enterprises that manufacture or use medical products and services, as well as to suppliers supplying raw materials, parts and services to these organizations.
The core idea of ISO13485:2016 is to meet the legal requirements for medical devices and maintain their safety and effectiveness, instead of pursuing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. The special requirements that differ from ISO9001 include:
1. ISO13485 is only applicable to the medical device industry defined within the scope of the standard, unlike ISO9001, which is a standard that can be adopted by all walks of life.
2.It highlights the conformity to laws and regulations, so the requirement for documented evidence information (documents and records) is very detailed in the standard. According to preliminary statistics, “documentation” is required at 56 places and “record retention” is required at 48 places in ISO13485:2016.
3.It emphasizes the requirements of product risk management, and requires the implementation of risk management for the entire life cycle of medical device products and services.
4.It emphasizes the supervision of products after they are marketed and the requirements for communicating with/reporting to the regulatory authorities;
For the above reasons, conformity to ISO13485 cannot be claimed as conformity to ISO9001.

Relationship between ISO13485 and medical device regulations in different countries
ISO13485:2016 has a wide range of applicability. This is because:
1. The formulation of the new version of the standard makes reference to the medical device regulations and regulatory requirements of relevant countries, such as QSR820 of the US.
2. China has equivalently transformed ISO13485:2016 into YY/T0287-2017, which is basically consistent with the Chinese Good Manufacturing Practice in terms of contents and requirements;
3. Similarly, the EU has equivalently transformed ENISO13485:2016, which combines with the EU regulations such as MDR EU (2017/745) to constitute the EU’s quality management system requirements for the CE product certification;
4. Medical device single audit program (MDSAP) is also based on ISO13485, adding the regulatory requirements of participating countries (the US (FDA), Australia (TGA), Brazil (ANVISA), Canada (HC), and Japan (MHLW)).
II. Service contents
Sungo’s professional team has more than ten years of quality management system consulting experience, and is familiar with the regulations of China, the EU, the UK, the US, Japan, Brazil, Australia, Canada and other countries and regions. Sungo crosses the abovementioned market regulatory thresholds for customers to ensure that products can enter the target markets successfully.
Our services include:
1. Accept the entrustment to audit the quality management systems of the customers’ suppliers in accordance with the laws and regulations of the countries and regions in which the target markets locate.
2.According to the customer requirements, conduct compliance diagnosis for the customers’ quality management systems, perform difference analysis, and propose rectification opinions;
3.Identify the international and regional regulatory requirements of the target markets and assist the customers in establishing the corresponding quality management systems.
4. Organize and integrate the international and regional regulatory requirements to help the customers establish integrated quality management systems;
5. Provide special services such as internal training, process development and validation, quality data analysis, and software verification according to the specific international and regional requirements for quality management systems;

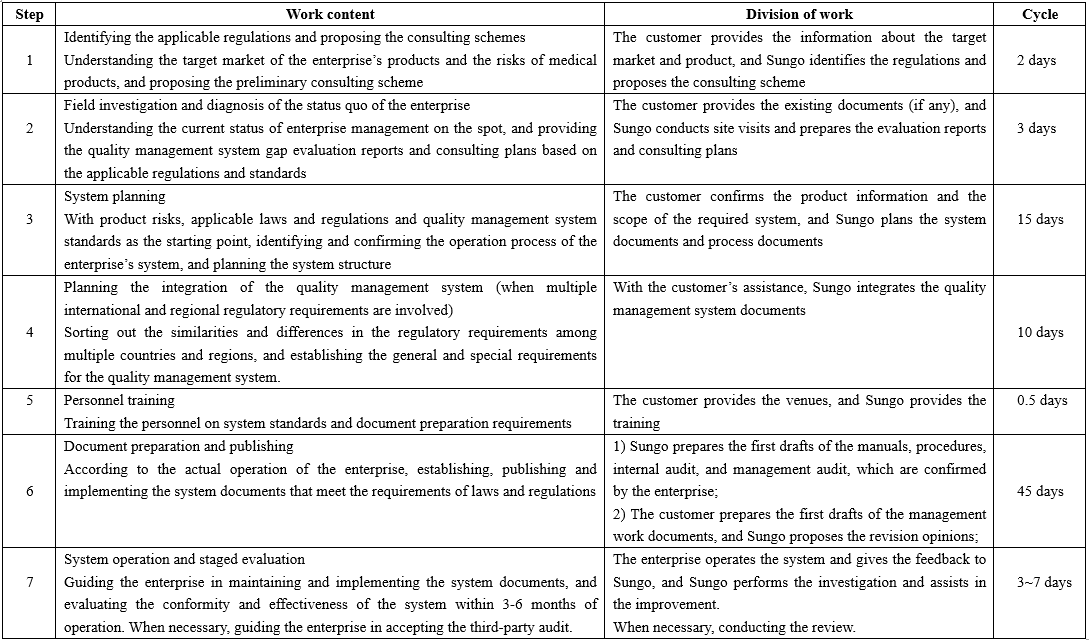
III. Service process